The Baltic countries, nestled along the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea, present a captivating tapestry of history, economic development, and cultural heritage. This exploration delves into the region’s rich past, examines its remarkable economic trajectory, and celebrates its vibrant cultural traditions.
From the medieval era to the present day, the Baltic countries have witnessed a succession of empires and nations vying for control. The region’s strategic location has shaped its destiny, leaving an imprint on its people, languages, and traditions.
Historical Overview of the Baltic Countries
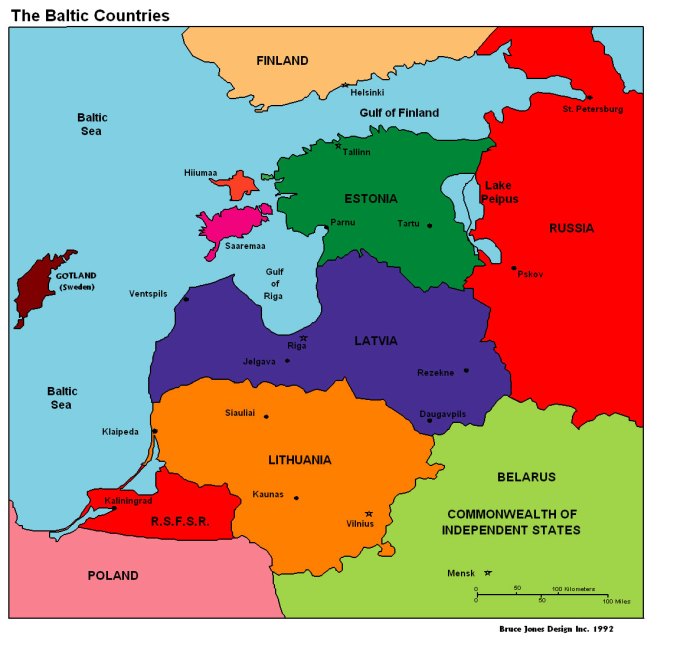
The Baltic region, encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, holds significant historical importance as a crossroads between Eastern and Western Europe. Throughout history, the region has witnessed numerous conquests and cultural exchanges, shaping its unique identity.
Key events in the history of the Baltic countries include:
- 12th-13th centuries: German crusaders establish control over the region, leading to the establishment of the Livonian Order.
- 16th century: The Reformation spreads through the Baltic region, resulting in the adoption of Lutheranism in Estonia and Latvia.
- 18th century: The Russian Empire gains control over the Baltic provinces.
- 1918: The Baltic countries declare independence following the Russian Revolution.
- 1940: The Soviet Union annexes the Baltic countries.
- 1991: The Baltic countries regain independence after the collapse of the Soviet Union.
The Baltic region is home to a diverse array of cultures and languages. Estonian, Latvian, and Lithuanian are the official languages of their respective countries, while Russian and other minority languages are also spoken.
Economic Development in the Baltic States: Baltic Countries
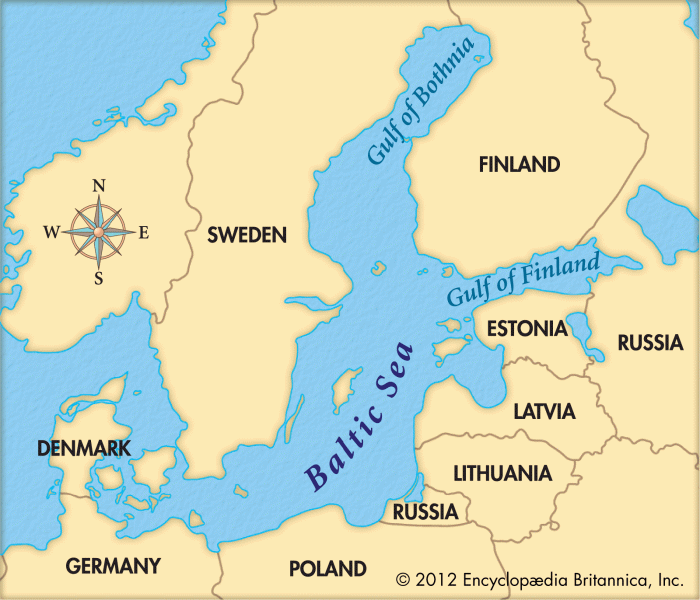
Following their independence in 1991, the Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania embarked on a journey of economic transformation, transitioning from centrally planned economies to market-based systems. Over the past three decades, these countries have achieved remarkable economic growth and development, becoming an integral part of the European Union and global economy.
The Baltic economies have consistently outperformed the EU average in terms of GDP growth. Estonia, in particular, has been a regional leader, with an average annual growth rate of over 4% since 2000. Latvia and Lithuania have also experienced significant growth, with average annual rates of over 3%.
The Baltics are a great place to visit for those interested in history and culture. The region is home to many medieval cities, castles, and churches. For a change of pace, consider a trip to Almeria , a city in southeastern Spain known for its beautiful beaches and Moorish architecture.
While Almeria offers a different experience than the Baltics, it is still a fascinating place to explore. The region’s unique blend of cultures is evident in its architecture, cuisine, and traditions. Visitors to the Baltics should be sure to add Almeria to their itinerary.
This economic growth has been driven by several factors, including:
- Foreign direct investment: The Baltic countries have attracted significant foreign investment, particularly in sectors such as manufacturing, transportation, and logistics.
- Export-oriented growth: The Baltic economies are heavily export-dependent, with a focus on high-value-added goods and services such as electronics, machinery, and pharmaceuticals.
- EU membership: Accession to the EU in 2004 provided the Baltic countries with access to the single market and EU funding, which has supported economic development and integration.
Despite their economic success, the Baltic countries face several challenges. These include:
- Demographic decline: The Baltic countries have experienced a decline in population due to emigration and low birth rates, which could impact future economic growth.
- Income inequality: While the Baltic economies have grown rapidly, income inequality has also increased, posing a challenge to social cohesion.
- Vulnerability to external shocks: The Baltic economies are heavily dependent on exports, making them vulnerable to external shocks such as global economic downturns.
Despite these challenges, the Baltic countries remain committed to economic development and integration. They are actively pursuing policies to address demographic decline, reduce income inequality, and diversify their economies. The Baltic countries are also working to strengthen their ties with the EU and other international partners.
The Baltics, with their pristine landscapes and rich history, are emerging as top luxury travel destinations. For those seeking exclusive experiences, top luxury travel destinations in the Baltics offer a perfect blend of history, culture, and natural beauty. From the medieval streets of Tallinn to the stunning beaches of the Curonian Spit, the Baltics offer a unique and unforgettable travel experience.
Political Landscape of the Baltic Region
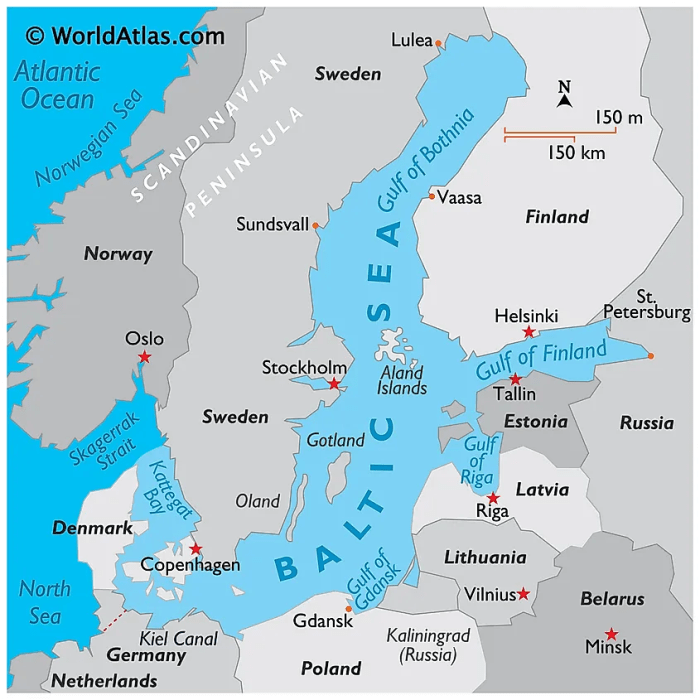
The Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania have undergone significant political transformations since regaining independence in 1991. These countries have established stable and democratic political systems, characterized by parliamentary democracies, rule of law, and protection of human rights.
Role of the European Union and NATO
The Baltic states have played an active role in European and international organizations, particularly the European Union (EU) and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). EU membership has fostered economic cooperation, political stability, and democratic values within the region. NATO membership, on the other hand, has strengthened the Baltic states’ defense capabilities and provided security guarantees against potential threats.
Current Political Issues and Challenges
Despite their political stability, the Baltic states face several ongoing challenges. These include:
- Regional security concerns: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine and Russia’s military presence in the Baltic Sea region have heightened security concerns in the Baltic states.
- Economic disparities: While the Baltic states have made significant economic progress, there are still disparities between urban and rural areas, as well as challenges related to income inequality.
- Demographic issues: The Baltic states are facing population decline and aging populations, which pose challenges for economic growth and social welfare systems.
- Political polarization: While the Baltic states have generally stable political systems, there are concerns about increasing political polarization and the rise of populist movements.
Cultural Heritage and Identity
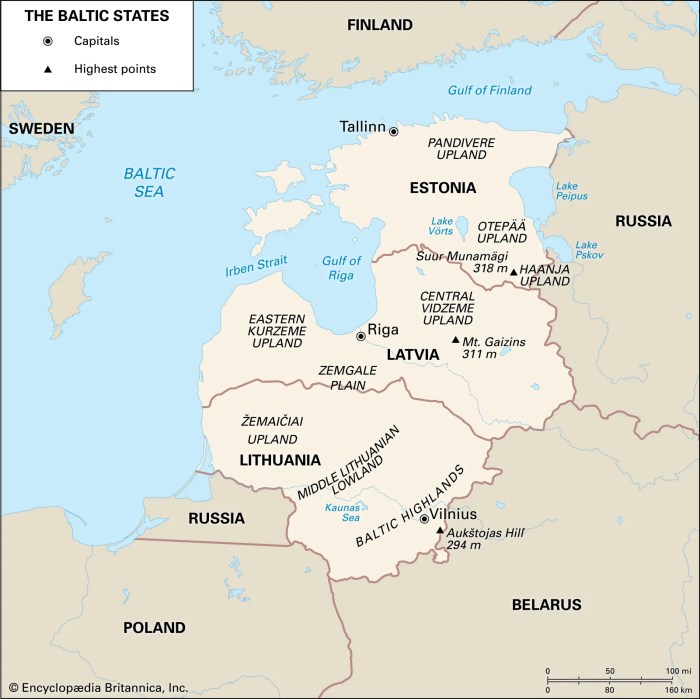
The Baltic countries, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, boast a rich and diverse cultural heritage that has been shaped by centuries of history, geography, and cultural exchange. From ancient folklore to vibrant art forms, the Baltic region is a treasure trove of cultural traditions that have played a pivotal role in shaping the national identities of its people.
Unique Traditions and Folklore
The Baltic countries are renowned for their unique traditions and folklore, which have been passed down through generations. Estonia, for example, is home to the ancient tradition of “runo singing,” a form of epic poetry that has been inscribed on the UNESCO Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity. Latvia is known for its vibrant folk festivals, such as the Ligo festival, which celebrates the summer solstice with bonfires, traditional costumes, and folk dancing. Lithuania, on the other hand, has a rich tradition of storytelling and mythology, which is reflected in its numerous folk tales and legends.
Art Forms
The Baltic countries have also produced a wealth of stunning art forms, from traditional crafts to contemporary masterpieces. Estonia is famous for its intricate textiles, such as the traditional “kirikutekk” quilts. Latvia is known for its amber jewelry, which is often used to create beautiful and unique pieces of art. Lithuania has a strong tradition of woodcarving, which can be seen in the elaborate churches and manor houses that dot the countryside.
Role of Culture in National Identity
Culture has played a crucial role in shaping the national identities of the Baltic peoples. During periods of foreign occupation and political turmoil, cultural traditions provided a sense of continuity and belonging. Today, the Baltic countries celebrate their cultural heritage with pride, and it remains an integral part of their national identities. From the ancient songs of Estonia to the vibrant festivals of Latvia and the rich mythology of Lithuania, the cultural heritage of the Baltic countries is a testament to the resilience and creativity of its people.
Regional Cooperation and Integration
The Baltic countries have fostered close regional cooperation and integration, establishing several initiatives and organizations to promote economic, political, and cultural collaboration.
The Baltic countries, known for their rich history and cultural heritage, have seen the rise and fall of many historical landmarks. While the region is not particularly renowned for its architectural wonders, one notable exception is the abbotsford convent in Scotland.
Despite its location outside the Baltic region, the convent’s historical significance and architectural beauty make it a worthwhile destination for anyone interested in exploring the broader cultural landscape of the Baltic countries.
One significant initiative is the Baltic Assembly, an inter-parliamentary organization established in 1991. It facilitates cooperation among the Baltic parliaments on various issues, including economic integration, security, and regional development.
Benefits of Regional Integration
- Enhanced economic growth and competitiveness through increased trade and investment.
- Improved infrastructure and connectivity, facilitating movement of goods and people.
- Increased political stability and security cooperation, addressing common challenges.
- Preservation and promotion of cultural heritage and identity, strengthening regional ties.
Challenges of Regional Integration
- Economic disparities and differing levels of development among the Baltic countries.
- Historical tensions and political differences, potentially hindering cooperation.
- Balancing regional integration with national sovereignty and interests.
- Managing the impact of regional cooperation on local communities and industries.
Impact of Regional Cooperation, Baltic countries
Regional cooperation has had a significant impact on the development of the Baltic region, contributing to:
- Increased economic prosperity and convergence among the Baltic countries.
- Enhanced regional security and stability, reducing tensions and fostering cooperation.
- Preservation and promotion of Baltic culture and identity, strengthening regional bonds.
- Improved infrastructure and connectivity, facilitating regional integration and economic development.
Closing Summary

As the Baltic countries continue to navigate the complexities of the 21st century, they stand as beacons of resilience and progress. Their economic growth, political stability, and cultural vitality serve as testaments to the region’s indomitable spirit. As they forge ahead, the Baltic countries promise to remain a source of fascination and inspiration for years to come.
General Inquiries
What is the historical significance of the Baltic region?
The Baltic region has been a crossroads of trade and conflict for centuries, with its strategic location connecting Eastern and Western Europe. It has been home to various civilizations, including the Vikings, Teutonic Knights, and Russian Empire.
How have the Baltic countries performed economically since independence?
Since regaining independence in 1991, the Baltic countries have experienced significant economic growth, driven by reforms, foreign investment, and integration into the European Union.
What are some of the unique cultural traditions of the Baltic countries?
The Baltic countries boast a rich cultural heritage, with distinct traditions in music, dance, folklore, and cuisine. They are known for their ancient song festivals, intricate amber jewelry, and traditional wooden architecture.